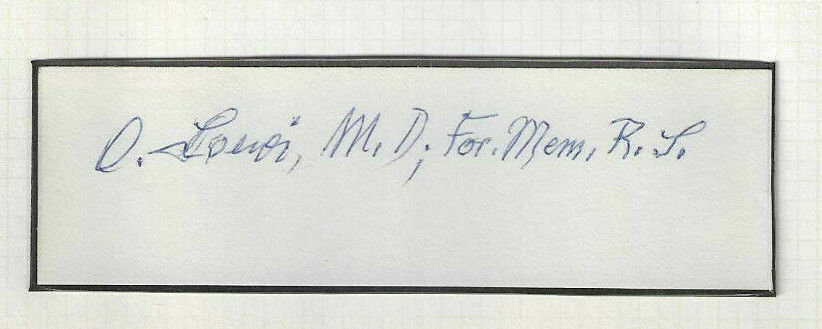-40%
RARE! “Protoplasm” Hugo von Mohl Hand Written Letter Todd Mueller COA
$ 369.59
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
Up for auction aRARE! “Protoplasm” Hugo von Mohl Hand Written Letter.
This item is authenticated By Todd Mueller Autographs and comes with their certificate of authenticity.
ES-457A
Hugo von Mohl
FFRS
H
FRSE
(8 April 1805 – 1 April 1872) was a German
botanist
from
Stuttgart
. He was the first person to use the word "
protoplasm
". He was a son of the
Württemberg
statesman
Benjamin Ferdinand von Mohl
(1766–1845), the family being connected on both sides with the higher class of state officials of Württemberg. While a pupil at the gymnasium, he pursued botany and mineralogy in his leisure time, till in 1823 he entered the
University of Tübingen
. After graduating with distinction in medicine he went to Munich, where he met a distinguished circle of botanists, and found ample material for research. This seems to have determined his career as a botanist, and he started in 1828 those anatomical investigations which continued till his death. In 1832 he was appointed professor of botany in Tübingen, a post which he never left. Unmarried, his pleasures were in his laboratory and library, and in perfecting optical apparatus and microscopic preparations, for which he showed extraordinary manual skill. He was largely a self-taught botanist from boyhood, and, little influenced in his opinions even by his teachers, preserved always his independence of view on scientific questions. He received many honours during his lifetime, and was elected foreign fellow of the
Royal Society
in 1868. The process of
cell division
as observed under a
microscope
was first discovered by Hugo von Mohl in 1835 as he worked on
green algae
Cladophora glomerata
. Mohl's writings cover a period of forty-four years; the most notable of them were republished in 1845 in a volume entitled
Vermischte Schriften
(For lists of his works see
Botanische Zeitung
, 1872, p. 576, and
Royal Soc. Catalogue
, 1870, vol. iv.) They dealt with a variety of subjects, but chiefly with the structure of the higher forms, including both rough anatomy and minute
histology
. The word
protoplasm
was his suggestion; the nucleus had already been recognized by
R. Brown
and others; but Mohl showed in 1844 that the protoplasm is the source of those movements which at that time excited so much attention. He recognized under the name of primordial utricle the protoplasmic lining of the vacuolated cell, and first described the behaviour of the protoplasm in cell division. These and other observations led to the overthrow of
Schleiden
's theory of origin of cells by free-cell-formation. His contributions to knowledge of the cell-wall were no less remarkable; he held the view now generally adopted of growth of cell-wall by apposition. He first explained the true nature of pits, and showed the cellular origin of vessels and of fibrous cells; he was, in fact, the true founder of the cell theory. Clearly the author of such researches was the man to collect into one volume the theory of cell-formation, and this he did in his treatise
Die vegetabilische Zelle
(1851), a short work translated into English (Ray Society, 1852). Mohl's early investigations on the structure of palms, of
cycads
, and of
tree ferns
permanently laid the foundation of all later knowledge of this subject: so also his work on
Isoetes
(1840). His later anatomical work was chiefly on the stems of
dicotyledons
and
gymnosperms
; in his observations on cork and bark he first explained the formation and origin of different types of
bark
, and corrected errors relating to lenticels. Following on his early demonstration of the origin of
stomata
(1838), he wrote a classical paper on their opening and closing (1850). In 1843 he started the weekly
Botanische Zeitung
in conjunction with
Schlechtendal
, which he edited jointly till his death. He was never a great writer of comprehensive works; no textbook exists in his name, and it would indeed appear from his withdrawal from co-operation in
Hofmeister
's
Handbuch
that he had a distaste for such efforts. In 1850, he was elected a foreign member of the
Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences
. In his latter years his productive activity fell off, doubtless through failing health, and he died suddenly at
Tübingen
on 1 April 1872. The standard
author abbreviation
Mohl
is used to indicate this person as the author when
citing
a
botanical name
.