-40%
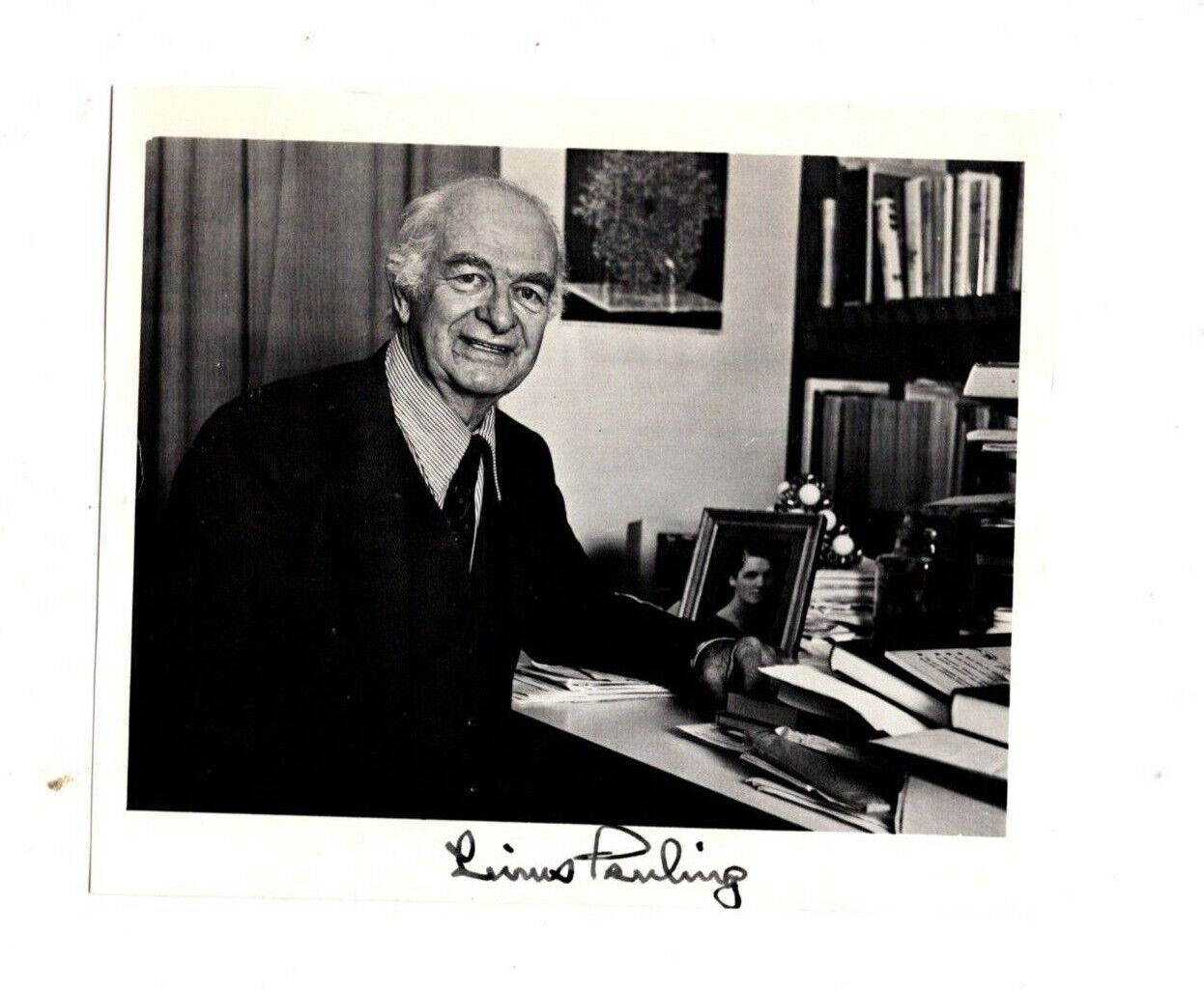
LINUS PAULING,SIGNED 6 3/4" x 5 3/4" PHOTO,WINNER OF NOBEL PEACE PRIZE,GENUINE
$ 25.87
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
Blank on Reverse.add .00 for 1st class/Insured to U.S....
Linus Pauling
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Linus Pauling
ForMemRS
Linus Pauling in 1962
Born
Linus Carl Pauling
February 28, 1901
Portland, Oregon
, U.S.
Died
August 19, 1994 (aged 93)
Big Sur
, California
Nationality
American
Education
Oregon State University
(BS)
California Institute of Technology
(PhD)
Known for
show
Spouse(s)
Ava Helen Miller
(
m.
1923
;
d.
1981
)
Children
4
Awards
ACS Award in Pure Chemistry
(1931)
Irving Langmuir Award
(1931)
Member of the National Academy of Sciences
(1933)
Davy Medal
(1947)
Nobel Prize in Chemistry
(1954)
Nobel Peace Prize
(1962)
Roebling Medal
(1967)
Lenin Peace Prize
(1968–69)
National Medal of Science
(1974)
Lomonosov Gold Medal
(1977)
NAS Award in Chemical Sciences
(1979)
Priestley Medal
(1984)
Vannevar Bush Award
(1989)
Scientific career
Fields
Quantum chemistry
Biochemistry
Institutions
As faculty member
Caltech
(1927–1963)
UC San Diego
(1967–1969)
Stanford
(1969–1975)
As fellow
Cornell University
(1937–1938)
University of Oxford
(1948)
Center for the Study of Democratic Institutions
(1963–1967)
Thesis
[
thesis
.library
.caltech
.edu
/1791
[3]
The Determination with X-Rays of the Structures of Crystals
]
(1925)
Doctoral advisor
Roscoe Dickinson
Richard Tolman
[1]
Other academic advisors
Arnold Sommerfeld
Niels Bohr
[2]
Doctoral students
Martin Karplus
Jerry Donohue
Matthew Meselson
Robert E. Rundle
Edgar Bright Wilson
William Lipscomb
[1]
Leonard Lerman
Signature
Notes
The only person to win two unshared Nobel Prizes.
Linus Carl Pauling
(
/
ˈ
p
ɔː
l
ɪ
ŋ
/
; 28 February 1901
–
19 August 1994)
[4]
was an American
chemist
,
biochemist
,
chemical engineer
,
peace activist
, author, and educator. He published more than 1,200 papers and books, of which about 850 dealt with scientific topics.
[5]
New Scientist
called him one of the 20 greatest scientists of all time,
[6]
and as of 2000, he was rated the 16th most important scientist in history.
[7]
For his scientific work, Pauling was awarded the
Nobel Prize in Chemistry
in 1954. For his peace activism, he was awarded the
Nobel Peace Prize
in 1962. He is one of four people to have won more than one Nobel Prize (the others being
Marie Curie
,
John Bardeen
and
Frederick Sanger
).
[8]
Of these, he is the only person to have been awarded two unshared Nobel Prizes,
[9]
and one of two people to be awarded Nobel Prizes in different fields, the other being
Marie Curie
.
[8]
Pauling was one of the founders of the fields of
quantum chemistry
and
molecular biology
.
[10]
His contributions to the theory of the chemical bond include the concept of
orbital hybridisation
and the first accurate scale of
electronegativities
of the elements. Pauling also worked on the structures of biological molecules, and showed the importance of the
alpha helix
and
beta sheet
in
protein secondary structure
. Pauling's approach combined methods and results from
X-ray crystallography
,
molecular model
building, and
quantum chemistry
. His discoveries inspired the work of
James Watson
,
Francis Crick
,
Maurice Wilkins
and
Rosalind Franklin
on the structure of DNA, which in turn made it possible for geneticists to crack the DNA code of all organisms.
[11]
In his later years he promoted
nuclear disarmament
, as well as
orthomolecular medicine
,
megavitamin therapy
,
[12]
and
dietary supplements
. None of his ideas concerning the medical usefulness of large doses of vitamins have gained much acceptance in the mainstream scientific community.
[6]
[13]
He was married to the American human rights activist
Ava Helen Pauling
.